|
बी एड - एम एड >> बी.एड. सेमेस्टर-1 प्रश्नपत्र-IV-B - वैल्यू एण्ड पीस एजुकेशन बी.एड. सेमेस्टर-1 प्रश्नपत्र-IV-B - वैल्यू एण्ड पीस एजुकेशनसरल प्रश्नोत्तर समूह
|
5 पाठक हैं |
||||||
बी.एड. सेमेस्टर-1 प्रश्नपत्र-IV-B - वैल्यू एण्ड पीस एजुकेशन (अंग्रेजी भाषा में)
Question- Explain the various types of Family Structure.
Answer -
What constitutes a family varies across the globe depending on a variety of factors including subsistence practices and economic behaviors. Family defines obligations that group members have to one another, both economically and socially. Generally, family members live together, but that is not always the case.
Types of Family Structure
We shall look at some of the types of family in this section :
Types of Family
Based on birth
• Family of orientation
• Family of procreation
Based on marriage
• Monogamous
• Polygynous
• Polyandrous
Based on residence
• Matrilocal
• Patrilocal
• Changing
Based on ancestry or descent
• Matrilineal
• Patrilineal
Based on nature of relation
• Conjugal
• Consanguine
Based on authority
• Matriarchal
• Patriarchal
Based on size or structure
• Nuclear
• Joint
• Extended
(i) Family of Orientation : The family in which an individual is born is his family of orientation.
(ii) Family of Procreation : The family where an individual sets up after his/her marriage is his/her family of procreation.
The family of orientation and procreation may live together under the same roof, but can still be distinguished.
(i) Monogamous Family : This family consists of one husband and wife, including children and is based on monogamous marriages.
(ii) Polygynous Family : A family consisting of one husband, and more than one wife, and all the children born to all the wives or adopted by each of them. This type of family has its basis in the polygynous form of marriage.
(iii) Polyandrous Family : A family made up of one wife and more than one husband, and the children, either born or adopted with each one of them. This family is based on polyandrous marriage.
(i) Family of Matrilocal Residence : When a couple stays in the wife’s house, the family is known as family of matrilocal residence.
(ii) Family of Patrilocal Residence : When a family stays in the house of husband, the family is known as family of patrilocal residence.
(iii) Family of Changing Residence : When a family stays in the husband’s house for some time, and moves to wife’s house, stays there for a period of time, and then moves back to husband’s parents, or starts living in another place, the family is called a family of changing residence.
(i) Matrilineal Family : When ancestry or descent is traced through the female line, or through the mother’s side, the family is called matrilineal family.
(ii) Patrilineal Family : A family in which the authority is carried down the male line, and descent is traced through the male line or the father’s side, is called a patrilineal family.
(i) Matriarchal Family : Matriarchal families are generally found in matrilineal societies. In these families, a woman is the head of the family, and authority is vested in her. Succession of property is through the female line, i.e., only daughters inherit the property.
After marriage, the husband resides in the wife’s house and descent is traced through the mother’s side. Here, children are brought up in mother’s house. Thus, in matriarchal societies, the matrilocal system exists. Matriarchal families are found only in matrilineal societies, which are very limited in number all over the world. They are found in parts of Latin America, Ceylon, parts of Africa and India (the Khasis and the Garos).
(ii) Patriarchal Family : Patriarchal families are commonly found in all parts of the world, since most societies in the world are patrilineal societies. In patriarchal families, the head of the family is a male, and authority is vested in him. Descent and property is passed through the male line and children are brought up in father’s house. Such families are patrilocal in nature.
(i) Conjugal Family : The conjugal family is made up of adults among whom there is a sexual relationship. It refers to a family system of spouses and their dependent children. The emphasis is placed on the marital relationship that exists between spouses. In modern times, the term ‘conjugal family’ is being used for partners, who have a long-term sexual relationship, but are not actually married.
(ii) Consanguine Family : A consanguine family is made up of members among whom a blood relation exists, or those who are consanguineal kin, i.e., a family consisting of parent(s) and children, or siblings (brothers, sisters, or brothers and sisters).
(i) Nuclear Family : A nuclear family is a small group consisting of a husband, a wife and children, natural or adopted. It is more or less an autonomous unit that is not under the control of adults or elders of the family. It consists of two generations only. In all modern societies, nuclear family is the most common type of family. In fact, nuclear family is both the consequence as well as the cause of the disintegration of joint family.
(ii) Joint Family : A joint family consists of three generation, living together under the same roof, sharing the same kitchen and purse or economic expenses. It is a family consisting of three nuclear families living together. According to Iravati Karve, a joint family is ‘a group of people, who generally live under the same roof, who eat food cooked at one hearth, who hold property in common, and who participate in common family worship and are related to each other as some particular type of kindered.
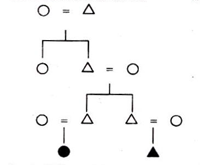
In fig. Ego (the shaded figure) is a part of a joint family consisting of four generations—the children, parents, grandparents and great-grandparents, all from the father’s side. These types of joint families are also known as patriarchal (father- centred) or patrilineal (lineage traced through the fathers or male side) joint families.
In such families, only unmarried daughters, or at times widowed daughters are a part of the family. Married daughters no longer belong to the family as they become a part of their husbands’ family. However, in the case of matriarchal joint families (mother centered) or matrilineal (lineage or descent traced through the mother’s side or the female side), daughters are a part of the joint family, whereas sons become a part of their wives’ families.
|
|||||













